Trademark registration in China is “registration first”, and companies that registered a trademark earlier can be allowed to register this trademark. Therefore, in order to protect your brand, please consider registering a Chinese trademark as soon as possible.
Why do I need to search before registering a Chinese trademark?
As of 2019, the number of valid trademark registrations in China exceeds 22.74 million, which is a huge number. Therefore, it is very important to search before registering trademarks to determine whether other companies have previously registered trademarks that are the same as or similar to the trademarks you want to register.
Considering the update frequency of the database, there may be a certain delay in the search results, and there is no doubt that searching through trademark lawyers can better judge the search results and obtain registration suggestions.
However, it is still necessary to know how to search for Chinese trademarks.
Chinese Trademark Office website
The China Trademark Office provides a free online search tool http://wcjs.sbj.cnipa.gov.cn/, click the “English” link in the upper right corner of the page to enter the English search interface.
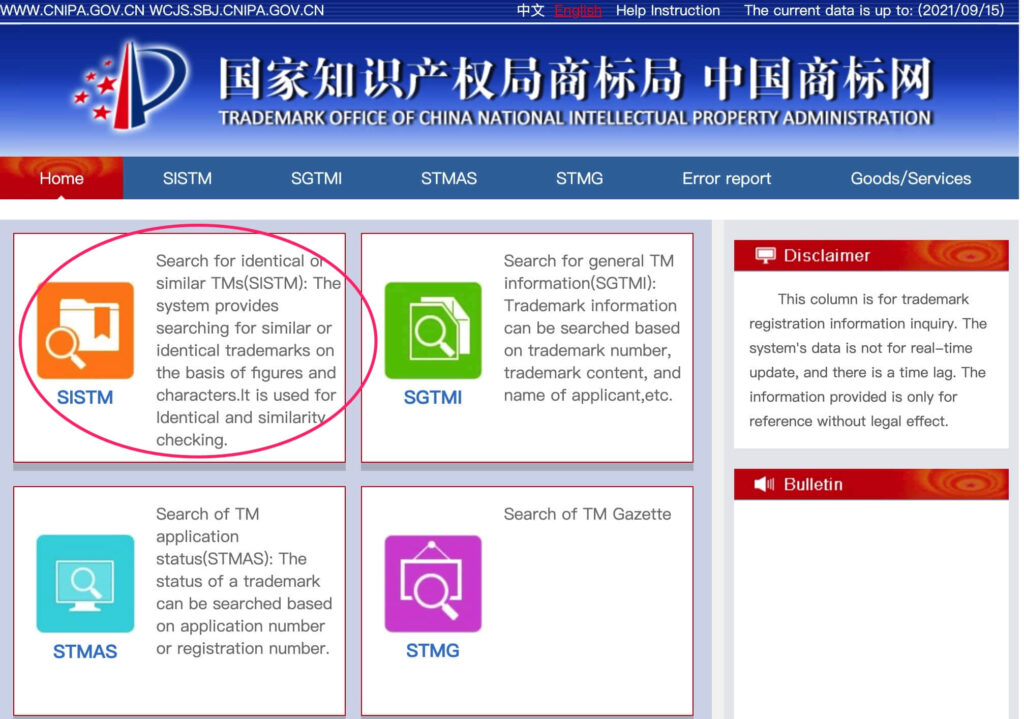
Search 1 – Searching for identical or similar trademarks (SISTM) in a single class
The ‘SISTM’ search tool allows you to search for identical or similar trademarks within a single class of goods or services. This is generally the most useful search tool.
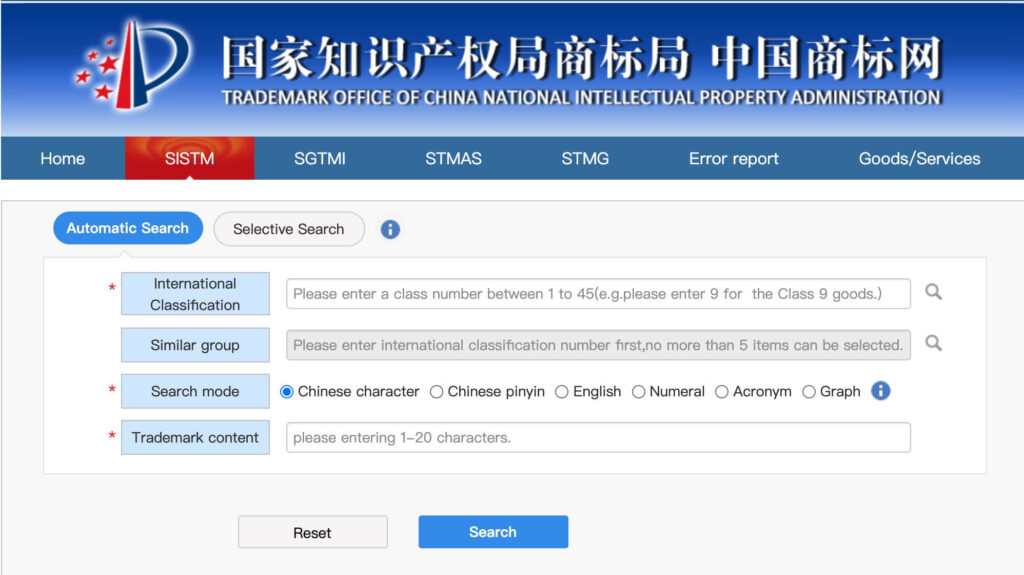
Support six searching methods: Chinese, Pinyin, English, Numbers, Initial, Graph.
Chinese character: please enter Chinese in the trademark name with no blanks.
Chinese pinyin: Please input Pinyin in the trademark search content with blanks between each Chinese character, for example: tong ren tang.
English: please enter 3 or more English letters in trademark name.(‘&’,‘.’or other characters are allowed.) selects the initial search method if less than 3 English letters.
Numeral: please entering Arabic Numberals in trademark name.
Acronym: please enter 1 or 2 English letters in trademark name. Select English search method if more than 2 English letters.
Graph: please enter code in graphical code, and separated with “;”, please get more details on the graphical code help page.
There are two search types – an ‘Automatic Search’ that uses default search settings and a ‘Selective Search’ that allows you to customize your search criteria. Choose ‘Automatic Search’.
International Classification: Chinese trademark registered trademarks adopt the internationally common “Distinguishing Table for Similar Goods and Services”, which includes a total of 45 categories, of which 34 are for goods and 11 are for service items. Trademarks are only granted exclusive rights in cases related to the goods or services they are registered with. For example, the trademark registration of medicines (belonging to Class 5) will not provide protection for medical devices (belonging to Class 10). Therefore, please choose the category of registration according to the goods you want to protect.
Similar group: China further divides trade marks into subclasses. ‘Similar Group’ indicates the Chinese subclass of the trade mark. Leave this field blank for your search.
Search mode: Select the appropriate option. You’ll usually be searching an English word.
Trademark content: Enter your search word(s), in English or Chinese. It doesn’t matter if the text is upper or lower case (i.e. Disney and DISNEY are treated the same).
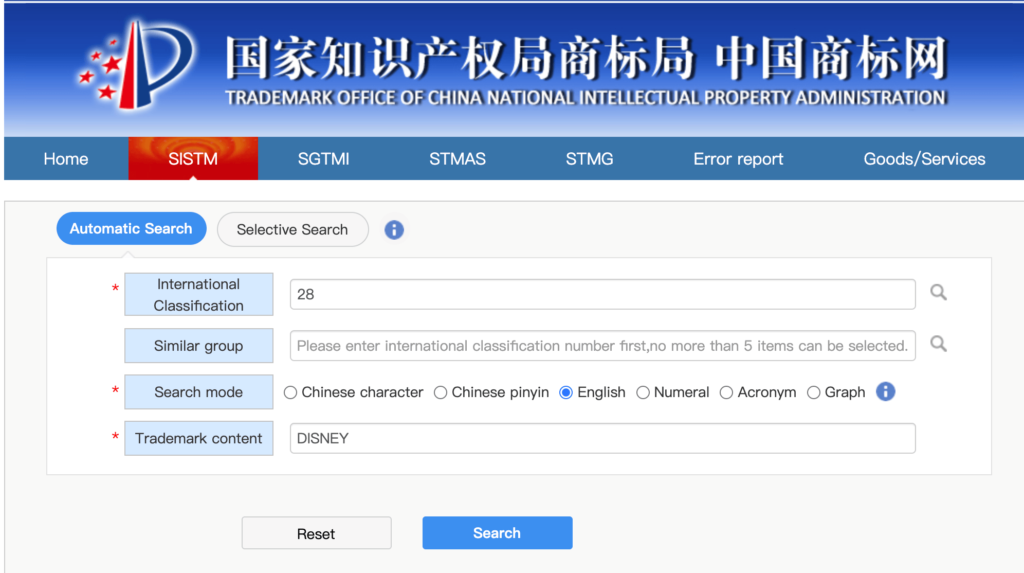
To illustrate, let’s try to search for “DISNEY”. We are interested in the toy category, which belongs to the International Classification 28 category, choose the search mode “English”.
Hit ‘Search’ and a new window will open displaying a list of identical and similar trade marks.
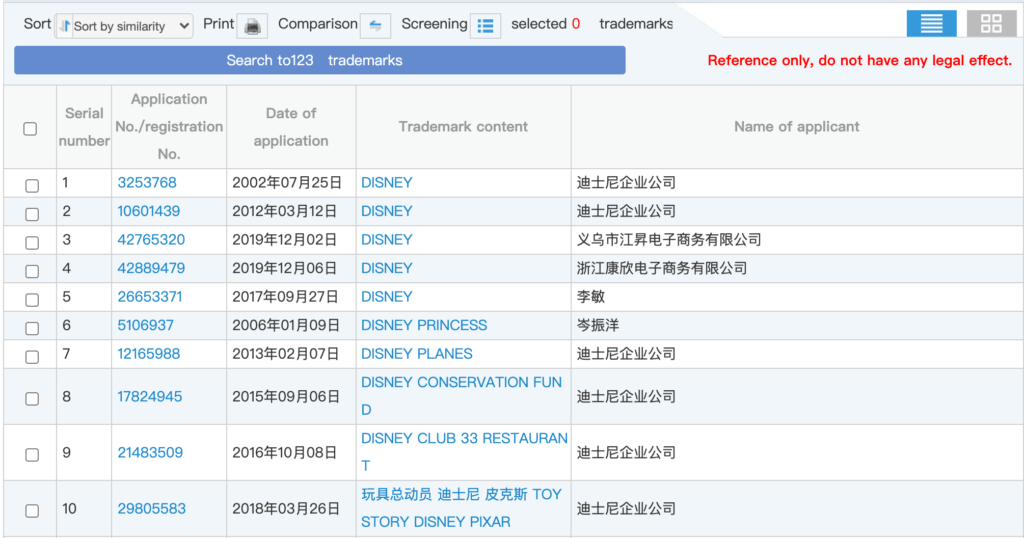
On the results page, you can also switch to the thumbnail view. This allows you to see how the trademark will look in the registry, including styled text and logos, without having to look at the trademark separately. This is important because when considering whether two trademarks are similar, you should consider not only the words used, but also the overall appearance of the trademark.

Clicking on any trademark name (list or thumbnail view) will open a new window showing details of the trademark, including protected goods/services and application/registration status.
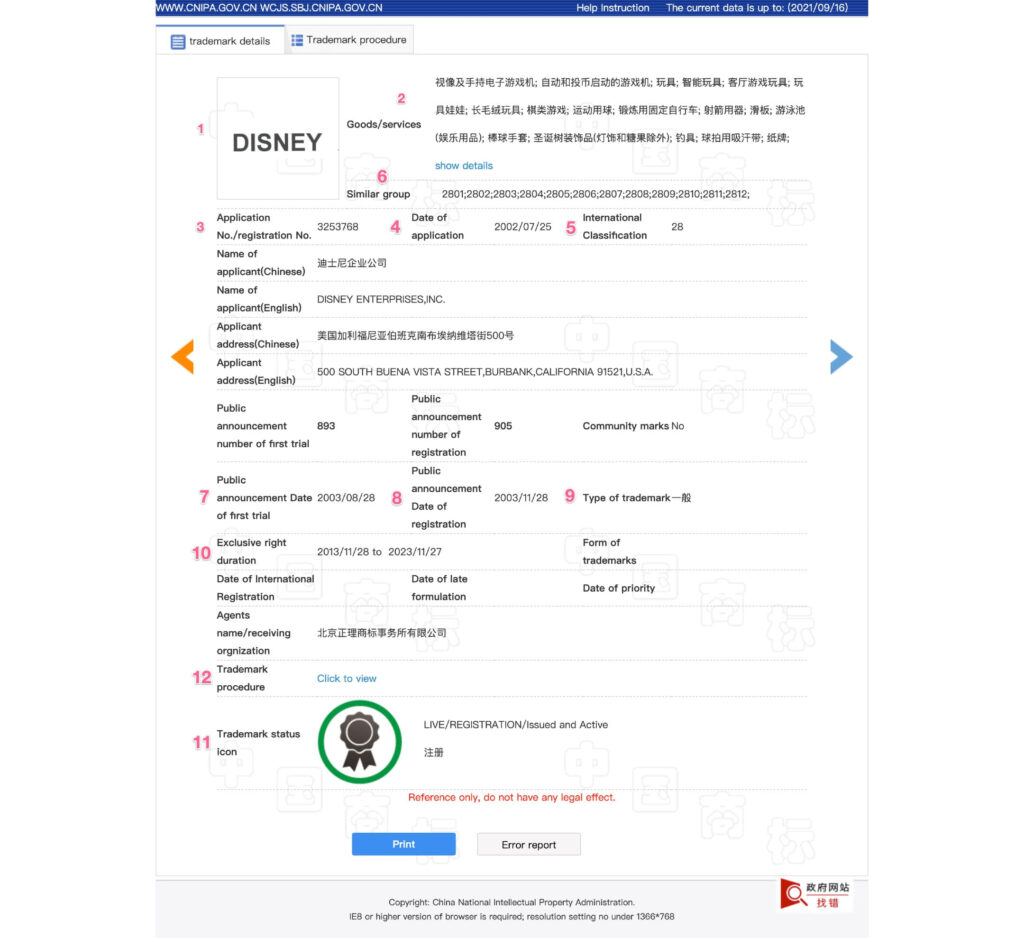
The detailed trademark information contains the following:
- Trademark image: The trademark itself, consisting of words, graphics or both.
- Goods/services: Shows a description of the goods or services covered by the trade mark. Currently the description is only available in Chinese.
- Application No./registration No.: Either the filing of each mark in each international class of goods or services assigns a unique number.
- Date of application: China has a first-to-file trade mark system. When there is a conflicting mark, the mark with the earliest application date (or priority date, if claimed) will have priority over the later filed mark.
- International classification: In our case, Disney registered toys, game consoles, board games belong to category 28.
- Similar Group: China further divides trademarks into several subcategories. “Similar Group” indicates the Chinese subcategory of trademarks, with the first two representing international classifications.
In China, subclasses are relatively complicated. Sometimes the registration of subclasses will not prevent the registration of similar subclasses, but there are also cases where similar subclasses across large categories prevents registration. - Public announcement, date of first trial: The date on which an application was accepted and published. This begins a three-month opposition period before the accepted trade mark is registered.
- Public announcement, date of registration: The date on which a trade mark was registered. If no opposition is filed within three months of acceptance of an application, or the opposition is unsuccessful, the accepted trade mark application is registered.
- Type of trade mark: Regular trademark, collective mark or certification mark
Collective marks are used in relation to goods or services provided by members of an association, for example SCOTCH WHISKY. Certification marks are used to certify the goods or services are of a particular origin, material, quality or other characteristic, for example TEQUILA. - Exclusive right duration: A trade mark is registered for 10 years from the registration date, and can be renewed indefinitely.
- Trademark status: The trade marks register shows pending applications as well as registered, lapsed and invalidated trade marks.
- Trademark procedure: Displays the full timeline of the registration procedure. This content is in Chinese only.
Search 2 – Searching multiple classes, applicant’s name, trade mark and trade mark number
If you want to search across multiple classes, or search by applicant’s name, trade mark or trade mark number, you should use the Search of General Trade Mark Information (SGTMI). You can search on the basis of any of the following five search criteria: International Classification, Application Number/Registration Number, Trademark Content (word), and Name of applicant in Chinese or English.

What next?
If you don’t find any conflicting trademarks, which is a good sign, consider filing a trademark as soon as possible and consult a trademark lawyer.
This search has limitations. Due to the update of the trademark database, there may be a certain delay in the data-there may be conflicting trademarks, but they have not been retrieved.
If you find an existing registration of the same or similar trademarks for similar goods or services, you have several options. If you believe that the trademark has not been used for three years since it was registered, you can file a lawsuit to cancel the non-use of the trademark. If you have strong evidence, you can oppose the application within a three-month objection period after acceptance, or apply to declare the registered trademark invalid (note that in both cases, it is difficult to successfully establish a good faith reason). In some cases, you can negotiate an acceptable price to buy the trademark from the owner, or obtain the owner’s consent – this is sometimes the most pragmatic option. Finally, you can develop a different brand for the Chinese market. A trademark lawyer can give you further advice.
In any case, you need professional advice from a trademark lawyer in this case, contact your trademark lawyer.


